
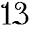
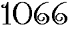
Edward was born in 1003. He was the last Saxon king to rule (for more
than a few months) in England. He is called "Edward the Confessor" to
distinguish him from another King of England, Edward the Martyr
(c962-979), who was assassinated (presumably by someone who wished to
place Edward's younger half-brother on the throne), and who came to be
regarded, on doubtful grounds, as a martyr for the faith. In Christian
biographies, the term "confessor" is often used to denote someone who has
born witness to the faith by his life, but who did not die as a martyr.
Edward was the son of King Ethelred the Unready. This does not mean that
he was unprepared, but rather that he was stubborn and wilful, and would
not accept "rede," meaning advice or counsel.
&Aelig;thelred was followed by several Danish kings of England, during whose rule young Edward and his mother took refuge in Normandy. But the last Danish king named Edward as his successor, and he was crowned in 1042. Opinions on his success as a king vary. Some historians consider him weak and indecisive, and say that his reign paved the way for the Norman Conquest. Others say that his prudent management gave England more than twenty years of peace and prosperity, with freedom from foreign domination, at a time when powerful neighbors might well have dominated a less adroit ruler. He was diligent in public and private worship, generous to the poor, and accessible to subjects who sought redress of grievances.
While in exile, he had vowed to make a pilgrimage to Rome if his family fortunes mended. However, his council told him that it was not expedient for him to be so long out of the country. Accordingly, he spent his pilgrimage money instead on the relief of the poor and the building of Westminster Abbey, which stands today (rebuilt in the thirteenth century) as one of the great churches of England, burial place of her kings and others deemed worthy of special honor.
He died on 5 January 1066, leaving no offspring; and after his death, the throne was claimed by his wife's brother, Harold the Saxon, and by William, Duke of Normandy. William defeated and slew Harold at the Battle of Hastings (14 October 1066), and thereafter the kings and upper classes of England were Norman-French rather than Anglo-Saxon. Edward is remembered, not on the day of his death, but on the anniversary of the moving ("translation") of his corpse to a new tomb, a date which is also the anniversary of the eve of the Battle of Hastings, the end of Saxon England.
O God, who didst call thy servant Edward to an an earthly Throne that he might advance thy heavenly kingdom, and didst give him zeal for thy Church and love for thy people: Mercifully grant that we who commemorate him this day may be fruitful in good works, and attain to the glorious crown of thy saints; through Jesus Christ our Lord, who liveth and reigneth with thee and the Holy Spirit, one God, for ever and ever.
O God, who called your servant Edward to an an earthly throne That he might advance your heavenly kingdom, and gave him zeal for your Church and love for your people: Mercifully grant that we who commemorate him this day may be fruitful in good works, and attain to the glorious crown of your saints; through Jesus Christ our Lord, who lives and reigns with you and the Holy Spirit, one God, for ever and ever.