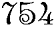

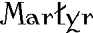
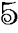
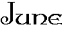
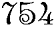
Wynfrith, nicknamed Boniface ("good deeds"), was born around 680 near
Crediton in Devonshire, England. When he was five, he listened to some
monks who were staying at his father's house. They had returned from a
mission to the pagans on the continent, and Boniface was so impressed by
them that he resolved to follow their example. Although his father had
intended him for a secular career, he gave way to his son's entreaties
and sent him at the age of seven to a monastery school. He eventually
became director of the school at Nursling, in Winchester, where he wrote
the first Latin grammar in England, and gave lectures that were widely
copied and circulated.
At thirty, he was ordained and set out to preach in Friesland (overlaps
with modern Holland), whence he was soon expelled because of war between
its heathen king and Charles Martel of France. Boniface, after a brief
withdrawal, went into Hesse and Bavaria, having secured the support of
the Pope and of Charles Martel for his work there. In Hesse, in the
presence of a large crowd of pagans, he cut down the Sacred Oak of
Geismar, a tree of immense age and girth, sacred to the god Thor. It is
said that after only a few blows of his axe, the tree tottered and
crashed to the ground, breaking into four pieces and revealing itself to
be rotted away within. It was the beginning of a highly successful
missionary effort, and the planting of a vigorous Christian church in
Germany, where Boniface was eventually consecrated bishop. He asked the
Christian Saxons of England to support his work among their kinsmen on
the continent, and they responded with money, books, supplies, and above
all, with a steady supply of monks to assist him in teaching and
preaching.
Boniface did not confine his attentions to Germany. He worked to
establish cooperation between the Pope and others in Italy on the one
hand and Charles and his successors in France on the other. He persuaded
Carloman and Pepin, the sons of Charles, to call synods for the reform of
the church in their territories, where under previous rulers bishoprics
had often been sold to the highest bidder. He never forgot his initial
failure in Friesland, and in old age resigned his bishopric and returned
to work there. Many Frisians had been converted earlier by Willibrord (another Saxon missionary from
England--see 7 Nov), but had lapsed after his death. Boniface preached
among them with considerable success. On June 5, the eve of Pentecost,
754, he was preparing a group of Frisians for confirmation when they were
attacked and killed by heathen warriors.
The historian Christopher Dawson estimates that he has had a greater
influence on the history of Europe than any other Englishman.
PRAYER (traditional language)
Almighty God, who didst call thy faithful servant Boniface to
be a witness and martyr in the lands of Germany and Friesland,
and by his labor and suffering didst raise up a people for
thine own possession: Pour forth thy Holy Spirit upon thy
Church in every land, that by the service and sacrifice of many
thy holy Name may be glorified and thy kingdom enlarged;
through Jesus Christ our Lord, who liveth and reigneth with
thee and the same Spirit, one God, for ever and ever.
PRAYER (contemporary language)
Almighty God, who called your faithful servant Boniface to be a
witness and martyr in the lands of Germany and Friesland, and
by his labor and suffering raised up a people for your own
possession: Pour forth your Holy Spirit upon your Church in
every land, that by the service and sacrifice of many your holy
Name may be glorified and your kingdom enlarged; through Jesus
Christ our Lord, who lives and reigns with you and the Holy
Spirit, one God, for ever and ever.
Psalm 115:1-8 or 31:1-5
Acts 20:17-28
Luke 24:44-53 (Ap)
Unless otherwise indicated, this biographical sketch was written by
James E.
Kiefer and any comments about its content should be directed to him.
The Biographical Sketches home page
has more information.